6 Key Stages of the ERP Implementation Life Cycle You Must Know
Introduction
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a transformative step for businesses aiming to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and achieve scalable growth. However, successful ERP implementation hinges on a clear understanding of its life cycle. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring the deployment meets organizational goals and delivers optimal ROI. This guide explores the six key stages of the ERP implementation life cycle, offering actionable insights for smooth execution.
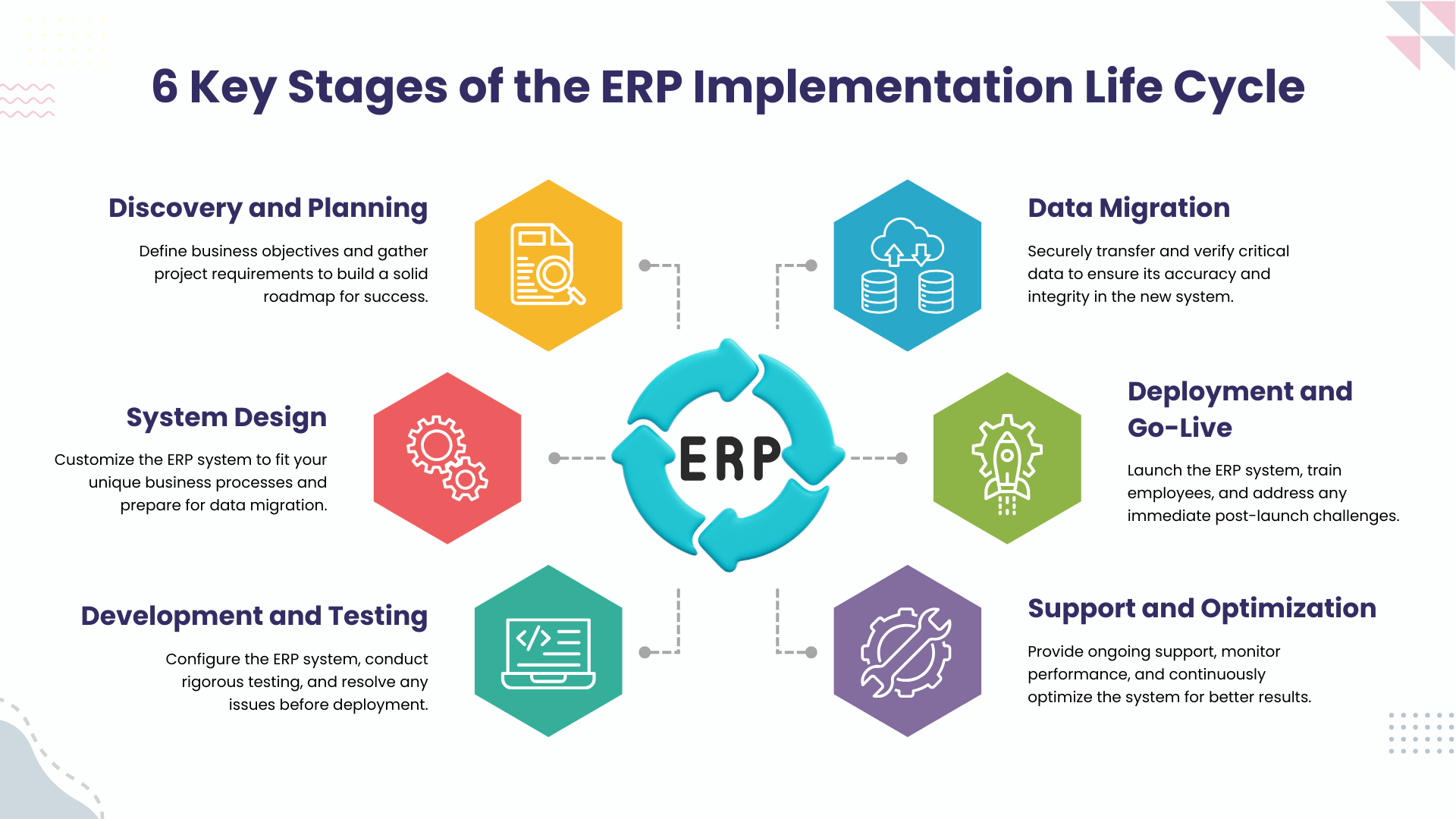
1. Discovery and Planning
The first step in ERP implementation is about understanding your organization’s specific needs and setting clear goals.
- Assess Business Needs: Conduct a comprehensive review of current processes and identify inefficiencies.
- Set Goals: Define measurable objectives such as reducing costs, improving workflow efficiency, or integrating systems.
- Assemble a Team: Build a cross-functional team with stakeholders from IT, finance, operations, and leadership.
- Create a Roadmap: Develop a timeline and project milestones to guide the implementation process.
2. System Design
System design focuses on tailoring the ERP solution to meet unique business requirements.
- Customization: Identify areas where the standard ERP functionality needs to be adjusted.
- Blueprint Creation: Draft a detailed plan outlining how the ERP will integrate with existing workflows.
- Data Migration Planning: Strategize how existing data will be migrated into the new system to ensure consistency and integrity.
3. Development and Testing
This stage involves configuring the system and ensuring it’s ready for deployment.
- System Configuration: Adjust the ERP system to match the organization’s workflows and processes.
- Conduct Testing: Perform rigorous testing, including unit tests, integration tests, and user acceptance tests, to identify and resolve bugs.
- Gather Feedback: Engage end-users to provide feedback, ensuring the system meets operational expectations.
4. Data Migration
A vital step that ensures accurate, clean data is transferred to the new system.
- Data Preparation: Cleanse and organize existing data to eliminate errors and duplicates.
- Data Import: Migrate critical business data, including customer information, inventory, and financial records.
- Verification: Cross-check the imported data to ensure accuracy and completeness.
5. Deployment and Go-Live
This stage marks the transition from planning to real-world use.
- System Rollout: Implement the ERP system across departments, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Employee Training: Conduct comprehensive training sessions to familiarize users with the new system.
- Issue Management: Monitor for any immediate technical or operational issues and address them promptly.
6. Support and Optimization
Post-implementation support ensures long-term success and continuous improvement.
- Provide Support: Offer end-user assistance through dedicated support teams or help desks.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly review system performance to ensure it meets business needs.
- Scale and Optimize: Introduce new features, address scalability requirements, and refine workflows as the business evolves.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the ERP implementation life cycle requires strategic planning, effective execution, and ongoing support. By understanding the six critical stages, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and fully leverage the benefits of ERP systems. Partnering with an experienced ERP provider can further enhance this process, ensuring a seamless and impactful transformation.

