Cloud ERP vs On-Premises ERP: 7 Key Differences Every SME Must Know
Introduction
Why SMEs Need ERP Solutions
In the fast-paced world of small and medium enterprises (SMEs), efficiency and adaptability are key to staying competitive. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for streamlining operations, improving decision-making, and fostering business growth. Whether it’s managing inventory, financials, or customer relationships, ERP systems offer a centralized platform to optimize these critical functions.
The Ongoing Debate: Cloud ERP vs. On-Premises ERP
A significant decision SMEs face is choosing between Cloud ERP and On-Premises ERP. Both options have their strengths and weaknesses, making the choice dependent on the unique needs and goals of the business. This guide explores the seven key differences to help SMEs make an informed decision.
1. What is Cloud ERP?
Definition and Key Features
Cloud ERP refers to an enterprise resource planning system hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. Key features include:
- Web-based access from any device.
- Automatic updates and patches.
- Subscription-based pricing model.
Common Use Cases for SMEs
- Businesses with remote or hybrid teams.
- Companies with fluctuating operational demands.
- Startups seeking cost-effective, scalable solutions.
2. What is On-Premises ERP?
Definition and Distinguishing Features
On-Premises ERP systems are installed and run on physical servers located within the company’s premises. Key attributes include:
- Direct control over hardware and software.
- Customizable to meet specific operational needs.
Typical Scenarios Where It Is Preferred
- Businesses with strict compliance requirements.
- Organizations that prioritize complete control over data.
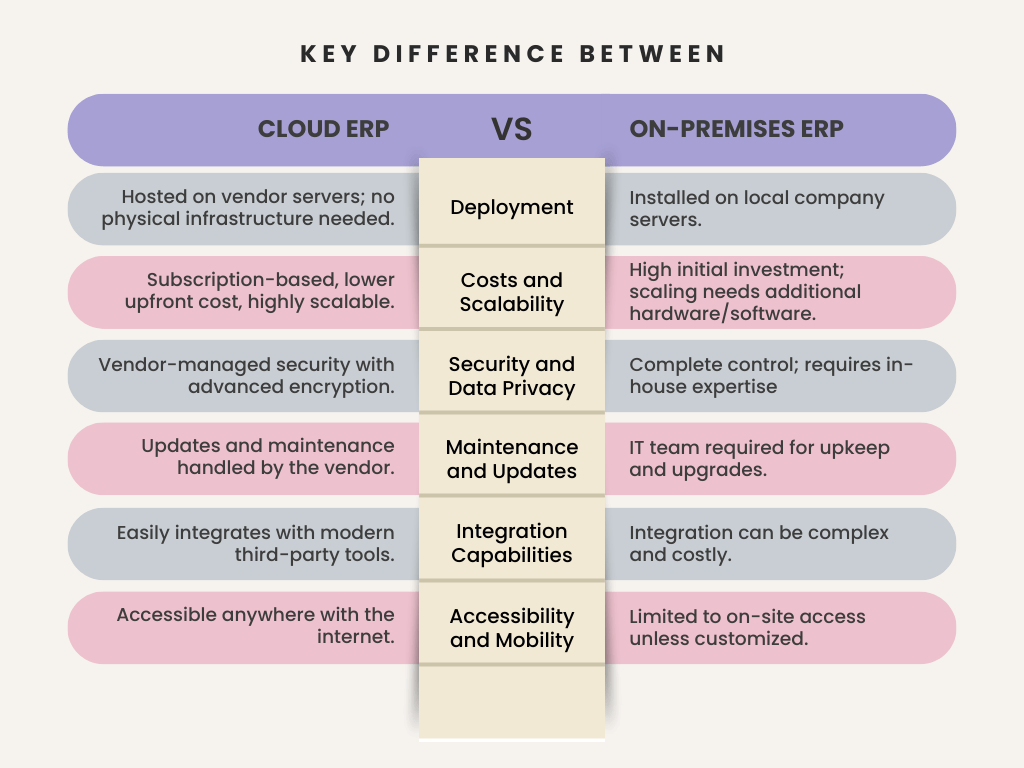
3. Key Differences Between Cloud ERP and On-Premises ERP
4. Advantages of Cloud ERP for SMEs
- Flexibility and Remote Access: Ideal for teams working across locations.
- Cost Efficiency for Growing Businesses: Avoids hefty upfront investments.
- Scalability for Dynamic Needs: Easily adapts to changing business requirements.
5. Limitations of Cloud ERP for SMEs
- Dependence on Internet Connectivity: Downtime can disrupt operations.
- Concerns Around Data Security: Sensitive data stored on third-party servers may raise compliance concerns.
6. Advantages of On-Premises ERP for SMEs
- Full Control Over Data and Infrastructure: Ideal for industries with stringent data regulations.
- No Ongoing Subscription Costs: Offers cost savings over time for long-term usage.
7. Challenges with On-Premises ERP for SMEs
- Higher Upfront Investment: Includes costs for hardware, software, and implementation.
- Limited Scalability and Mobility: Expansion often requires significant infrastructure upgrades.
8. Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Cloud and On-Premises ERP
Business Size and Budget
- Smaller businesses often benefit from the affordability of Cloud ERP.
- Larger organizations with dedicated IT teams may prefer On-Premises ERP.
Industry-Specific Needs
- Industries with compliance-heavy requirements might lean towards On-Premises ERP.
- Dynamic industries may find Cloud ERP more suitable.
Growth Projections
- Companies anticipating rapid growth may prefer the scalability of Cloud ERP.
Conclusion
Both Cloud ERP and On-Premises ERP offer unique advantages and challenges. While Cloud ERP is ideal for SMEs seeking flexibility and scalability, On-Premises ERP provides greater control and customization. By assessing business size, industry requirements, and long-term goals, SMEs can select the ERP system that best supports their growth and operational efficiency.

